The amount of pre-ejaculation released.
Functions performed by preseed
Risks associated with pre-semen release
There have been no large-scale studies to determine the sperm content in pre-semen, but some small studies have shown the presence of sperm in pre-semen.
Increases the formation of pre-ejaculate
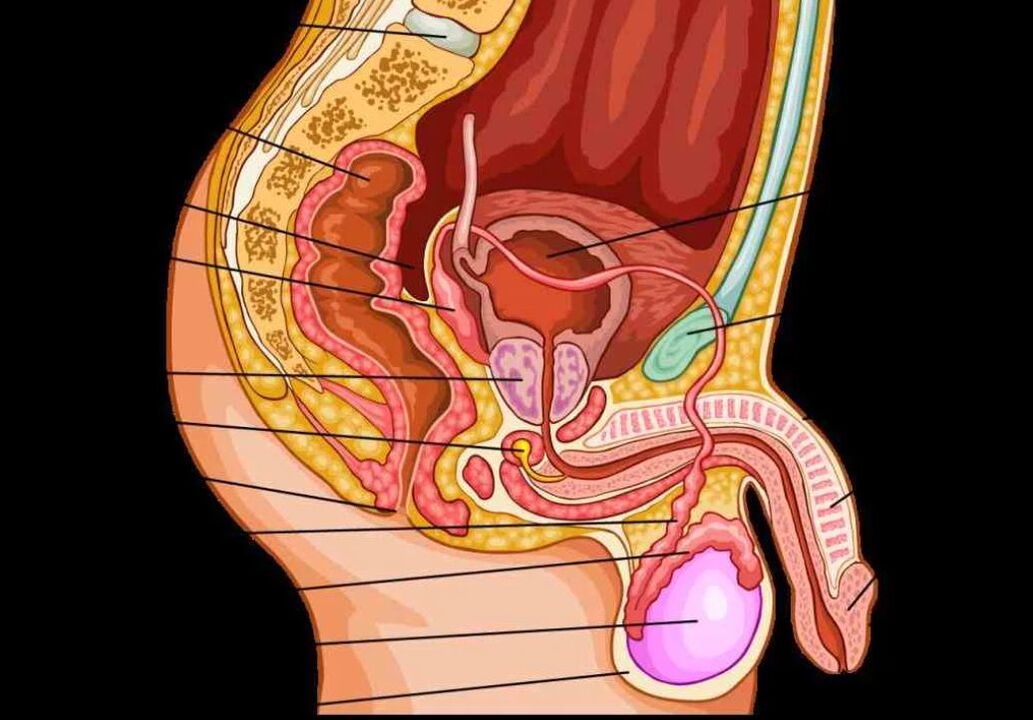
The discharge during male sexual excitement is called pre-ejaculation. When a man is excited, it protrudes from the urethral opening. Presemen is secreted by the bulbourethral and Littre glands, which are distributed along the entire length of the tube from the external opening of the bladder to the bladder neck.
- Ensure semen passes freely through the urethra;
- Destroy bacteria;
- Moisturizes and inhibits the acidic environment in the urethra.

- odorless;
- transparency;
- viscosity;
- No lumps or inclusions;
- Does not cause unpleasant or painful feelings.
- Fluid appears in the urethra during the day;
- An unpleasant odor occurs;
- pain during urination;
- excessive mucus formation;
- lubrication is released voluntarily without sexual arousal;
- the presence of third-party inclusions;
- The consistency changes to too thick or liquid.
| nocturnal emissions | Random leakage of sperm without orgasm. The cause of this process is a decrease in muscle tone of the vas deferens. Pathology due to chronic inflammation |
| Bleeding | Drain the lubricant mixed with blood. Urethral mucosal damage occurs |
| Leukocyte urethral leakage | The exudative phase of the inflammatory process, caused by thermal, mechanical, chemical, or viral damage to the urethral mucosa |
| Mucopurulent | They consist of small amounts of white blood cells, serous fluid, and glandular secretions. This mucus is characterized by active formation at night. A man noticed pus discharge and yellow spots on his underwear in the morning. Mucopurulent discharge occurs when the urethra is damaged by bacteria: Trichomonas, Ureaplasma, Chlamydia |
| Purulent | They include large numbers of leukocytes, urothelium, mucus, and serous fluid. They have a thick consistency and an unpleasant odor. They appear as yellow or green droplets. Evidence for the development of gonococcal urethritis, which develops in the context of chlamydia and gonorrhea |

occurrence of natural secretions
Emission indicators are within the normal range
In most cases, this change is indicative of pathological changes, although there are exceptions.
- Transparent water color;
- No obvious unpleasant odor;
- Medium thickness.
Changes in secretions are a sign of disease
- Inflammation of the urinary tract caused by proliferation of pathological microorganisms;
- Infections spread through intimate relationships;
- malignant formation;
- postoperative problems;
- Urogenital organ damage.
- Prostatic leakage;
- Balanoposthitis;
- hematuria;
- Nongonococcal urethritis.
Male discharge: normal or abnormal?
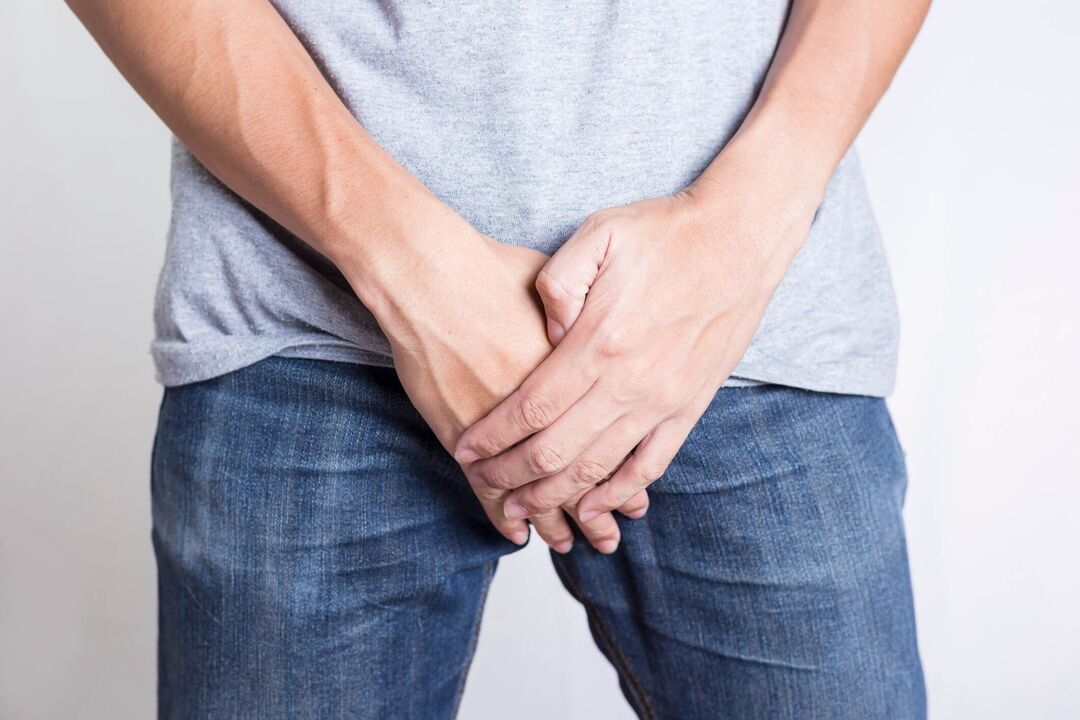

Physiological discharge during excitement
Norm or deviation?
- No unpleasant odor;
- Transparent color;
- Medium consistency.
- disease;
- Nutritional characteristics (food consumed);
- abstinence from sexual activity;
- Stress and poor lifestyle reduce immunity.
- The result of changes in the own pathogenic flora (not dangerous, but medical supervision is required, since against the background of an increased number of bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms, the risk of disease and inflammation increases);
- sexually transmitted infections;
- Tumors, cancer diseases—neoplastic processes;
- Caused by injury, penile curvature or other physiological acquired or congenital diseases;
- Consequences of surgical intervention (requiring special methods and more careful monitoring).
| Classification criteria | feature |
| The distribution amount can be: |
|
| Press highlight color: |
|
| By consistency: | |
| Discharge frequency: |
|
- Cause (disease, infection, inflammation, etc. );
- severity (how advanced the disease is);
- immunity;
- concomitant diseases;
- Duration of the cause.
discharged from hospital due to sexually transmitted disease
- Chlamydia;
- Mycoplasmosis;
- Ureaplasmosis.
- Trichomoniasis;
- Chlamydia;
- Ureaplasmosis.
Discharge during inflammation
- Streptococcus;
- Candida;
- E. coli;
- staphylococcus
- Presence of mucus;
- Presence of pus;
- viscosity;
- Turbidity.
treat

in conclusion
- The normal state of the fluid secreted by the glans penis is clear and white, with no unpleasant odor, pus or blood.
- Disturbed secretions may indicate the development of inflammatory processes associated with sexually transmitted infections as well as sexually transmitted diseases.
- The characteristics of symptoms may depend on the duration of the development of the disease, its characteristics and the immunity of the man.